|
|
1 жил өмнө | |
|---|---|---|
| media | 1 жил өмнө | |
| README.md | 1 жил өмнө | |
| docker-compose.yml | 1 жил өмнө | |
| tasks.py | 1 жил өмнө |
README.md
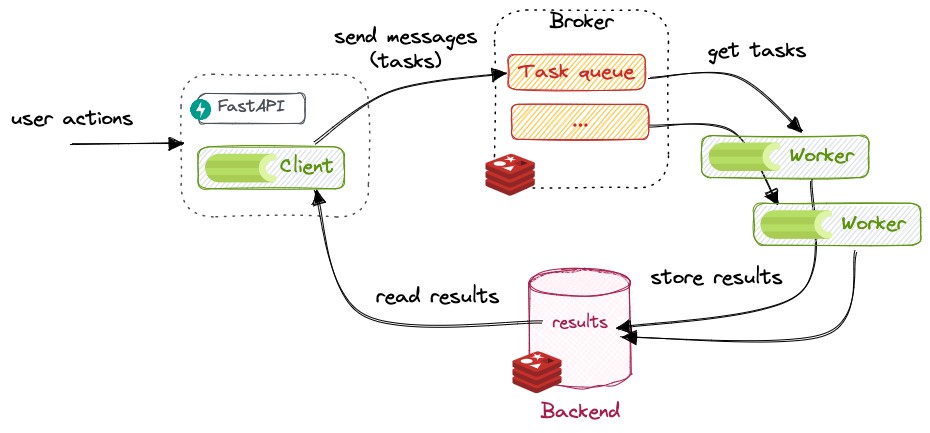
Redis-Celery (Distributed Architecture)
This includes
- Redis
- Flower
Usage (docker-compose)
start the system
add ``` -d ``` run in background * down the system ctrl-c ordocker-compose down ```
Celery
Celery Documentation
Flower Documentation
install Celery
pip install -U "celery[redis]"
Starting the worker
celery -A proj worker
Options
Worker Options:
-n, --hostname HOSTNAME Set custom hostname (e.g., 'w1@%%h').
Expands: %%h (hostname), %%n (name) and %%d, (domain).
-D, --detach Start worker as a background process.
-S, --statedb PATH Path to the state database. The extension
'.db' may be appended to the filename.
-l, --loglevel [DEBUG|INFO|WARNING|ERROR|CRITICAL|FATAL]
Logging level.
-O, --optimization [default|fair]
Apply optimization profile.
--prefetch-multiplier <prefetch multiplier>
Set custom prefetch multiplier value for
this worker instance.
Pool Options:
-c, --concurrency <concurrency>
Number of child processes processing the
queue. The default is the number of CPUs
available on your system.
celery worker --help can get more infomation.
woker in Windows
add --pool=solo option
Calling the task
>>> from tasks import hello
>>> hello.delay()
If your celery app set rsult backend
>>> from tasks import hello
>>> result = hello.delay()
The ready() method returns whether the task has finished processing or not:
>>> result.ready()
>>> False
You can wait for the result to complete, but this is rarely used since it turns the asynchronous call into a synchronous one:
>>> result.get(timeout=1)
>>> 'hello world'